With data security becoming paramount for almost everyone, encryption is one of the more important technology terms you will need to know. Since data security has to be a priority--not just for your business--but for you, understanding what encryption is, and how its used can put you in a better position to understand tomorrow’s security solutions. For this week’s tip, we will take you inside cryptography, and more specifically, data and network encryption.
What is Cryptography?
Simply put, cryptography is the art (or science) of writing or solving written or generated codes. Cryptography is the strategy of using a predefined key to convert data into a format that is indecipherable. Since no entity can view the information without the key, the information secured by encryption is able to be stored and transmitted securely. To decode the message, you need a cipher or a key.
A Short History of Cryptography
As long as there has been human communication, there have been secrets. The first known evidence of the use of cryptography was found carved in hieroglyphics on a wall in Egypt, and has subsequently been used throughout human history to send and receive secret messages.
Centuries later, Julius Caesar was known to use a form of substitution cipher that shifts each letter three spots in the alphabet to encode a message. In fact, there are some that still call this type of cipher a Caesar cipher. The Caesar cipher looks like this:
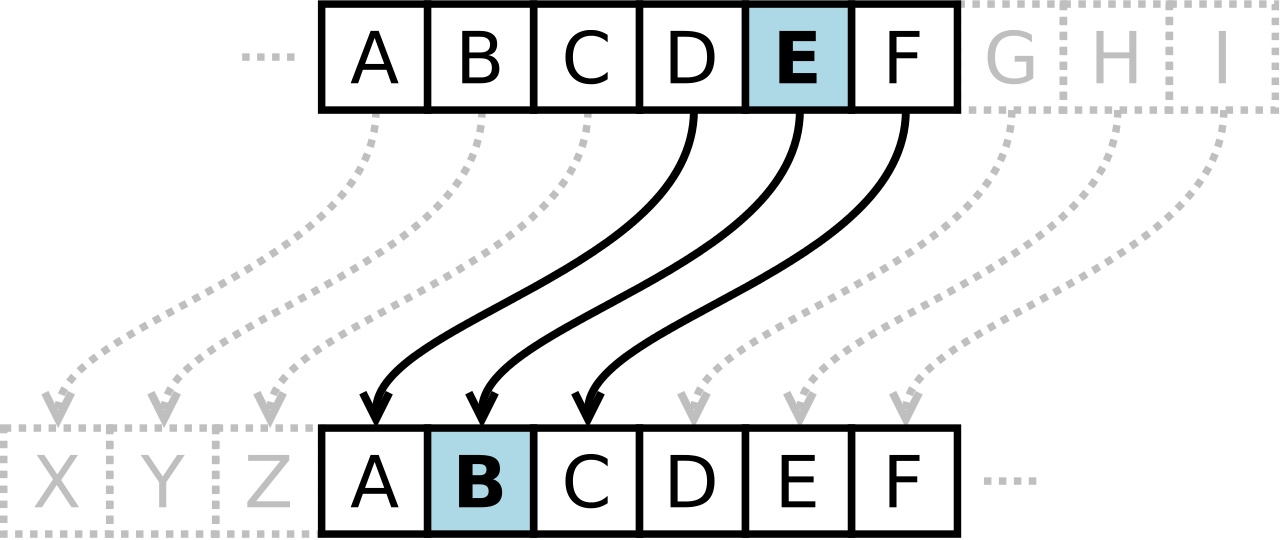
It’s clear that this type of cipher is dependent on the secrecy around the system, not a dedicated key to unlock the cipher. Once the system is known, these basic codes become known almost immediately. In fact, most substitution ciphers can be broken with a simple pad and paper.
This changed in the 16th century when Giovan Battista Bellaso came up with an improvement by using a series of interwoven ciphers. The process was misattributed to Blaise de Vigenère, and has since been referred to as the Vigenère cipher.
Despite all the coded messages sent and received over the centuries, cryptography as we know it has only come into fashion over the past century as technological advancements have facilitated more sophisticated methods of encryption. In the early 20th century, Edward Hebern, while sitting in jail for stealing a horse, came up with a method of encryption using an old typewriter fashioned with a rotor. The purpose was to turn what to the user was a simple Caesar cipher into a Vigenère cipher with the use of Hebern’s two-way rotor machine. A user would push a key and the rotor would provide the corresponding substitution key to decrypt the message. 
If this machine started modern encryption, Enigma changed it forever. Shortly after Hebern’s invention, German engineer Arthur Scherbius innovatively built what was essentially a Hebern device with multiple rotors and called it Enigma. For a decade German naval superiority over mainland Europe had as much to do with their ability to send and receive coded messages as it did to their manufacturing might.
Modern Encryption
When we speak of encryption today, we are just talking about the same type of thing that Hebern and Scherbius were doing: cloaking data to provide privacy or security to the parties involved in the correspondence. Today, data is worth more than ever; as a result businesses are spending more on their encryption solutions.
All businesses collect a fair amount of personally identifiable information (PII). This information includes names, birth dates, Social Security numbers, and financial and medical information. The liability companies have today is immense, as they can (and often are) sued if a customer, employee, or vendor’s PII is stolen and leaked or shared.
The modern business uses several types of encryption. Individual file encryption encrypts specific data; volume encryption secures a container where files and folders can be stored; and, full-disk encryption secures all the information on a computer or server. To ensure that the data is protected from theft, encrypting all the information deemed sensitive should be a priority.
In order for your business’ encryption initiatives to be successful, there are some best practices that users need to know. One is password security. Often the key to your encrypted information is a simple password. In order to mitigate risk and keep encryption working for you, there are some password management tips you should adhere to. Following these will keep your encrypted data, and your business safe. They include:
- Use passwords with eight characters or more.
- Use different passwords for different files, computers, and systems.
- Change your passwords frequently.
- Utilize upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols in your passwords.
- Don’t use common words or phrases.
- Don’t use words spelled backwards, common misspellings, or abbreviations.
More Encryption
Other than your standard protection against the loss of data, there are security solutions that allow you to encrypt communications you have with your customers, staff, and vendors. Email encryption has become an essential business tool. Many of today’s enterprise email solutions come with options to encrypt your messages, keeping communications secure.
Another way encryption is leveraged by the modern business is with the use of a virtual private network (VPN). The VPN offers users who are outside of a network to get an encrypted and secure pathway to share and receive files from a centralized server. Remote file exchange is important for many businesses, and the use of VPNs can go a long way toward quelling the risks inherent in this process.
Types of Encryption Finally, understanding what types of encryption there are can help you understand what position your organization is in, in regards to file, server, and communication security. The types of encryption used today include:
- Triple DES - Designed as a replacement to the single Data Encryption Standard (DES) that doesn’t hold up against the tools modern hackers have. Triple DES uses three individual keys with 56 bits each, which in total adds up to 168 bits, however experts place it closer to 112 bits of key strength.
- RSA - RSA is a public-key encryption algorithm and is currently the standard for secure transmission of data over the Internet. Since it uses two keys, a public key to encrypt it and a secure private key to decrypt it, it makes it very difficult for hackers to decipher.
- Blowfish - Designed to replace DES, Blowfish is a symmetric cipher that splits messages into blocks of 64 bits and encrypts them individually. As a result, it is extraordinarily secure and often used in e-commerce platforms and password managers.
- Twofish - The developer of Blowfish has released Twofish as a faster option that makes it a perfect encryption tool for hardware and software systems.
- AES - Available in 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit options, the Advanced Encryption Standard is basically uncrackable. Used by governments and other organizations that deal in extraordinarily sensitive information, AES has begun to become the standard in encryption due to its impenetrable record.
Data security is more important today than ever. At XFER, our knowledgeable technicians can help your organization come up with data and network security plan that is sure to keep your data safe, and keep your business running efficiently. To learn more, don’t hesitate to call us today at 734-927-6666 / 800-GET-XFER.
![]()



